AI technology has become an incredibly important part of most IT functions. One of the many reasons IT professionals are investing in AI is to fortify their digital security.
One of the best ways that cybersecurity professionals are leveraging AI is by utilizing SAST strategies.
AI Solidifies Network Security with Better SAST Protocols
AI technology has led to a number of new cybersecurity threats. Fortunately, organizations can also use AI technology to fight cybercrime as well.
Every single day, a wide variety of new applications and lines of code are being released. A big part of what enables this constant deployment of new applications is a testing process known as static application security testing, or SAST. It analyzes the source code created by developers or organizations to locate security flaws. An application is analyzed by SAST prior to having its code built. It is frequently referred to as “white box testing.”
These days, organizations wish to adopt the shift left method, which requires problems to be corrected as soon as they are discovered. Because of this, SAST takes place extremely early on in the software development lifecycle (SDLC).
AI has made it easier than ever for IT networks to improve SAST. Neil K. Jones discussed the role of artificial intelligence in SAST development in his post titled The Magic of AI in Static Application Security Testing in Dzone.
This works because SAST does not require a well-functioning software; rather, it simply needs machine learning codes that are currently being developed, which it then analyzes to find vulnerabilities. These AI codes also help developers detect SAST vulnerabilities in the early stages of development, so they may quickly resolve the issues without releasing vulnerable code into production, which could pose a threat to the infrastructure of the company.
For modern-day applications that use containers and Kubernetes, SAST is used for Kubernetes security to protect deployments by identifying potential vulnerabilities in the codebase before the code is put into production. This allows organizations to fix issues early on and prevents any potential vulnerabilities from affecting the final product. This is one of the best ways for companies to use AI to improve network security.
How Does a Modern SAST Strategy Work and What Role Does AI Play in It?
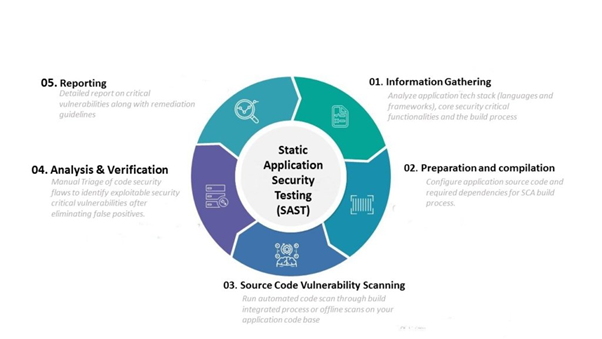
The present SAST technique is quite well developed, especially as it has improved due to new advances in AI. This technology also helps it make use of a wide variety of tools, all of which contribute to the process of fixing smaller bugs and vulnerabilities that may exist in the code.
There are a number of potential vulnerabilities that need to be addressed, such as open source supply chain attacks, that could happen because of things like outdated packages. New developments in AI have made it easier to detect these problems, which helps improve the security of the overall application.
What are some of the ways that AI has helped improve SAST? Some of the benefits have been developed by AI scientists at IBM.
These experts used IBM’s AI application known as “Watson” to better identify security vulnerabilities. They came up with an Intelligent Finding Analytics (IFA) tool, which had a 98% accuracy with detecting security vulnerabilities.
You can learn more about the benefits of using AI for SAST in the following YouTube video by IBM.
Let’s have a conversation about the approaches that are currently being taken to address problems of this nature.
Securing the Dependencies
Applications rely on a large number of different dependencies in order to function properly. Not only do they make the task easier for the software developers, but they also assist developers in writing code that is reliable and effective. Due to the fact that the majority of these dependencies are open source and therefore could include vulnerabilities, it is necessary to perform regular updates on them.
There could be a large number of dependents within an application. Thus, it is impossible for those dependencies to be monitored manually. Doing so would involve a significant amount of effort and could also lead to errors caused by manual intervention. In light of this, businesses typically make use of dependency management tools.
Such tools, after checking for available updates in the dependencies within a predetermined amount of time, open a pull request for each update that is available. They are also able to combine requests if that has been permitted by the user. Therefore, they find ways to eliminate the risks associated with the dependencies.
Performing Code Reviews
Code is the sole determinant of an application’s behavior, and errors in the code are the root cause of security flaws. If these vulnerabilities were to be sent to production, they might create a wide variety of problems, such as SQL injection, and could even compromise the infrastructure of the entire organization. Because of this, it is absolutely necessary to use the shift-left technique before putting code into production.
A significant number of SAST tools are being utilized by organizations for the purpose of deploying code reviews. These code review tools perform an in-depth analysis of the code before it is added to any repository. If the code has any of the known vulnerabilities, they will not allow it to be deployed until the flaws have been fixed. Therefore, it is useful for the shift-left strategy, which is based on the concept of remedying a vulnerability as soon as it is discovered, and only pushing secure code into production.
There is a large variety of softwares available on the market, and some of them enable companies and other organizations to patch their code as soon as security flaws are found. The patch can be deployed with just a few mouse clicks, and there are often several distinct options available to choose from when fixing a particular vulnerability.
Secret Scannings
These days, application are dependent on a significant amount of integration, such as payment gateways, error detection, and so on. In most cases, these APIs will execute, and authentication will be carried out using the API key and the secret.
These keys ought to be required to have an adequate level of security, such as the Live API key for Stripe payment needing to have an adequate level of protection. If this information is leaked, anybody can access the sensitive payment data and withdraw or view it. As a result, several businesses have begun using secret scanning tools.
These tools basically go through the code to see whether it contains any of the known API keys; if it does, the tool prevents the code from being published into production. It is possible for the code review tool itself to provide these features. Alternatively, an organization may easily write their own proprietary tool in order to identify problems of this kind.
AI Makes SAST More Effective than Ever
Companies are using AI technology to deal with a host of new cybersecurity threats. One of the best applications of AI is by using new SAST protocols to identify security threats.
Since companies are now transitioning to a shift-left strategy, they are employing SAST tools, which, in a nutshell, discover vulnerabilities as soon as they are coded and fix them. This is causing the shift left approach to become increasingly popular. If the code has any flaws that could be exploited by malicious actors, the deployment will be blocked until the problems are fixed.
Companies now have access to a wide variety of different methods, such as dependency management tools, secret scanning tools, and so on, which not only produce the proper secure code deployment but also produce the proper patches for vulnerabilities as soon as they are discovered in the coding phase.